As a developer, we are all aware of the git init command, which quickly turns your project folder into a version-controlled repository irrespective of the programming language or the type of file you are using.
Similarly, In Docker version 4.18 or above you can make use of the docker init command to create Docker-related starter files for your project.
Syntax:
docker init [OPTIONS]Example: git init command
- Let's create a project folder.
% mkdir myPythonProject % cd myPythonProject - Now let's run the
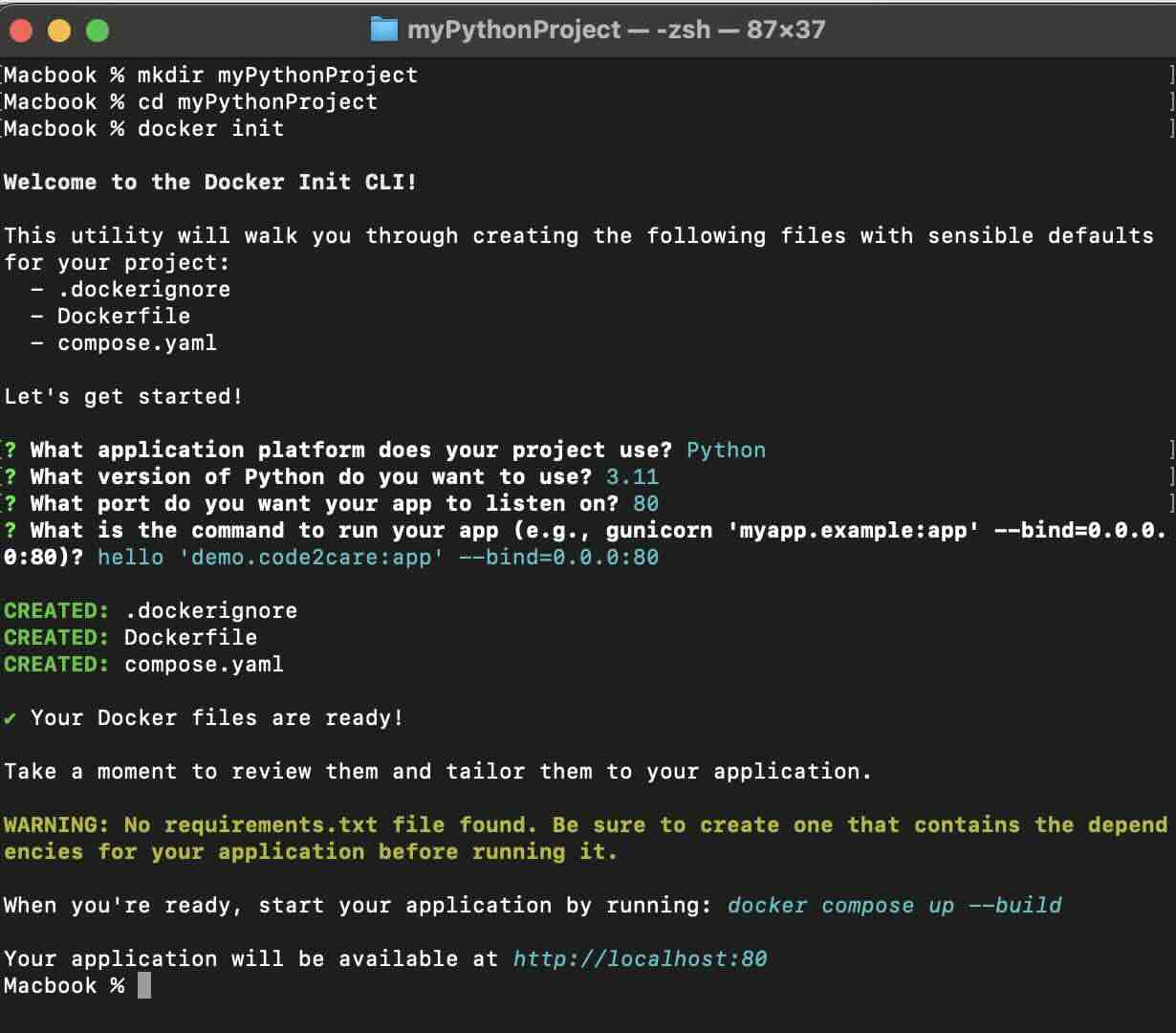
git initcommand inside it.% docker init Welcome to the Docker Init CLI! This utility will walk you through creating the following files with sensible defaults for your project: - .dockerignore - Dockerfile - compose.yaml Let's get started! ? What application platform does your project use? [Use arrows to move, type to filter] Go - suitable for a Go server application > Python - suitable for a Python server application Node - suitable for a Node server application Rust - suitable for a Rust server application ASP.NET - suitable for an ASP.NET application Other - general purpose starting point for containerizing your application Don't see something you need? Let us know! QuitLet's choose Python.
? What application platform does your project use? Python ? What version of Python do you want to use? 3.11 ? What port do you want your app to listen on? 80 ? What is the command to run your app (e.g., gunicorn 'myapp.example:app' --bind=0.0.0.0:80)? hello 'demo.code2care:app' --bind=0.0.0:80 CREATED: .dockerignore CREATED: Dockerfile CREATED: compose.yaml ✔ Your Docker files are ready! Take a moment to review them and tailor them to your application. WARNING: No requirements.txt file found. Be sure to create one that contains the dependencies for your application before running it. When you're ready, start your application by running: docker compose up --build Your application will be available at http://localhost:80 - As you can see, the docker init command creates dockerignore, Dockerfile and compose.yaml as well as the install all dependencies based on rerequirements.txt file in this case.
- Finally it also deploys the application at http://localhost:80
Created Dockerfile
# syntax=docker/dockerfile:1
# Comments are provided throughout this file to help you get started.
# If you need more help, visit the Dockerfile reference guide at
# https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/builder/
ARG PYTHON_VERSION=3.11
FROM python:${PYTHON_VERSION}-slim as base
# Prevents Python from writing pyc files.
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
# Keeps Python from buffering stdout and stderr to avoid situations where
# the application crashes without emitting any logs due to buffering.
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1
WORKDIR /app
# Create a non-privileged user that the app will run under.
# See https://docs.docker.com/develop/develop-images/dockerfile_best-practices/#user
ARG UID=10001
RUN adduser \
--disabled-password \
--gecos "" \
--home "/nonexistent" \
--shell "/sbin/nologin" \
--no-create-home \
--uid "${UID}" \
appuser
# Download dependencies as a separate step to take advantage of Docker's caching.
# Leverage a cache mount to /root/.cache/pip to speed up subsequent builds.
# Leverage a bind mount to requirements.txt to avoid having to copy them into
# into this layer.
RUN --mount=type=cache,target=/root/.cache/pip \
--mount=type=bind,source=requirements.txt,target=requirements.txt \
python -m pip install -r requirements.txt
# Switch to the non-privileged user to run the application.
USER appuser
# Copy the source code into the container.
COPY . .
# Expose the port that the application listens on.
EXPOSE 80
# Run the application.
CMD hello 'demo.code2care:app' --bind=0.0.0:80Created compose.yaml
# Comments are provided throughout this file to help you get started.
# If you need more help, visit the Docker compose reference guide at
# https://docs.docker.com/compose/compose-file/
# Here the instructions define your application as a service called "server".
# This service is built from the Dockerfile in the current directory.
# You can add other services your application may depend on here, such as a
# database or a cache. For examples, see the Awesome Compose repository:
# https://github.com/docker/awesome-compose
services:
server:
build:
context: .
ports:
- 80:80
# The commented out section below is an example of how to define a PostgreSQL
# database that your application can use. `depends_on` tells Docker Compose to
# start the database before your application. The `db-data` volume persists the
# database data between container restarts. The `db-password` secret is used
# to set the database password. You must create `db/password.txt` and add
# a password of your choosing to it before running `docker compose up`.
# depends_on:
# db:
# condition: service_healthy
# db:
# image: postgres
# restart: always
# user: postgres
# secrets:
# - db-password
# volumes:
# - db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
# environment:
# - POSTGRES_DB=example
# - POSTGRES_PASSWORD_FILE=/run/secrets/db-password
# expose:
# - 5432
# healthcheck:
# test: [ "CMD", "pg_isready" ]
# interval: 10s
# timeout: 5s
# retries: 5
# volumes:
# db-data:
# secrets:
# db-password:
# file: db/password.txtFacing issues? Have Questions? Post them here! I am happy to answer!
Author Info:
Rakesh (He/Him) has over 14+ years of experience in Web and Application development. He is the author of insightful How-To articles for Code2care.
Follow him on: X
You can also reach out to him via e-mail: rakesh@code2care.org
More Posts related to Docker,
- Install Docker on Mac using brew cask
- How to know the Docker Sandbox ID of a Container Network?
- How to Rename Docker Image with none TAG and REPOSITORY?
- How to know list of images available on your device
- Docker Alpine Linux and Apache2 Example
- Install Bash on Alpine Linux - Docker
- Docker Run Command Examples - Part 1
- Install the minimal Linux on Docker (only 5 mb Alpine Linux)
- [fix] docker: Error response from daemon: dial unix docker.raw.sock: connect: no such file or directory.
- Install RabbitMQ on Docker
- How to know docker Engine details
- [Fix] Docker Error response from daemon: manifest for :latest not found: manifest unknown
- How to stop and start a docker container
- How to create volume in Docker using Command
- How to know the Docker Engine Version
- [docker] Error response from daemon: No such container
- Install Docker for Mac using Home-brew Cask
- Docker - Incompatible CPU detected - M1/M2 Mac (macOS Sonoma)
- [fix] Docker Desktop App not starting on Mac (macOS)
- Unable to find image docker latest locally
- How to Stop/Cancel/kill docker image pull
- List of what's new in Docker 4.23
- [Docker M1/M2 Mac] qemu-x86_64: Could not open /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2: No such file or directory AWS CLI
- Install Docker Desktop on M1/M2 Apple Silicon ARM Chip Mac
- Docker - Running in Resource Saver mode
More Posts:
- How to Split a String using delimiter in Python - Python
- How to install micro text editor using brew on macOS - MacOS
- How to change default browser on Mac Monterey - MacOS
- How to enable Dark Mode in Windows 11 - Windows-11
- How to Change Java JDK Version in IntelliJ IDE - Java
- How to know the Serial Number of MacBook on macOS Ventura 13.0 - MacOS
- Send Extra Data with Ajax Get or Post Request - JavaScript
- Facebook : Warning: Request without access token missing application ID or client token - Facebook
