In Java 8 java.util.function package you will find the Predicate.java Functional Interface which is a boolean-valued function which takes one argument and returns a boolean, lets see some examples,
Java Predicate Examples:- 1: Check if provided input is of type String
- 2: Check if provided input is of null
- 3: Check if provided input String is declared
- 4: Check if age is over 18 or not
- 5: Check if array contains inputted String.
- 6: Check if provided input has length > 4 or not
- 7: Predicate with changing with default or method
- 8: Predicate with Stream filter
Example 1:
package org.code2care;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
*
* Use of Predicate to check if the provided input
* to test function is a String or not
*
*/
public class PredicateExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String string = "Java";
int integer = 10;
Boolean bool = true;
Predicate<Object> isString = object -> (object instanceof String);
System.out.println(isString.test(string));
System.out.println(isString.test(integer));
System.out.println(isString.test(bool));
}
}true
false
false
Example 2:
package com.company;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
*
* Use of Predicate to check if the provided input
* as is null or not
*
*/
public class PredicateExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = null;
String str2 = "Java";
Predicate<Object> isDefined = s -> (s == null);
System.out.println(isDefined.test(str1));
System.out.println(isDefined.test(str2));
}
}true
false
Example 3:
package com.company;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
*
* Use of Predicate to check if the provided input
* to declared or not
*
*/
public class PredicateExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = null;
String str2 = " ";
String str3 = "";
String str4 = "Java";
Predicate<String> isDefined = s -> (s == null || "".equals(s.trim()));
System.out.println(isDefined.test(str1));
System.out.println(isDefined.test(str2));
System.out.println(isDefined.test(str3));
System.out.println(isDefined.test(str4));
}
}true
true
true
false
Example 4:
package com.company;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
*
* Use of Predicate to check if the provided input
* as age is greater than 18 or not
*
*/
public class PredicateExample4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age1 = 12;
int age2 = 18;
int age3 = 22;
Predicate<Integer> isAbove18 = s -> (s > 18);
System.out.println(isAbove18.test(age1));
System.out.println(isAbove18.test(age2));
System.out.println(isAbove18.test(age3));
}
}false
false
true
Example 5:
package com.company;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
*
* Use of Predicate to check if the provided input
* is available in a Collection List or not
*
*/
public class PredicateExample5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> countries = new ArrayList<>();
countries.add("Japan");
countries.add("China");
countries.add("USA");
countries.add("France");
countries.add("Australia");
countries.add("Sweden");
Predicate<String> isInCountriesList = country -> (countries.contains(country));
String country1 = "Canada";
String country2 = "India";
String country3 = "Sweden";
System.out.println(isInCountriesList.test(country1));
System.out.println(isInCountriesList.test(country2));
System.out.println(isInCountriesList.test(country3));
}
}false
false
true
Example 6:
package com.company;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
*
* Use of Predicate to check if the provided input
* has the length as required
*
*/
public class PredicateExample6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Java";
String s2 = "Python";
String s3 = "PHP";
String s4 = "Scala";
String s5 = "Swift";
Predicate<String> isLengthGreaterThan4 = string -> (string.length() > 4);
System.out.println(isLengthGreaterThan4.test(s1));
System.out.println(isLengthGreaterThan4.test(s2));
System.out.println(isLengthGreaterThan4.test(s3));
System.out.println(isLengthGreaterThan4.test(s4));
System.out.println(isLengthGreaterThan4.test(s5));
}
}false
false
false
true
true
Example 7:
package com.company;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
*
* Predicate With Chaining with or default function
*
*/
public class PredicateExample7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Cool";
String s2 = "Dude";
String s3 = "Awesome";
Predicate<String> startsWithC = (string) -> (string.toLowerCase().startsWith("c"));
Predicate<String> startsWithD = (string) -> (string.toLowerCase().startsWith("d"));
Predicate<String> startsWithCorD = startsWithC.or(startsWithD);
System.out.println(startsWithCorD.test(s1));
System.out.println(startsWithCorD.test(s2));
System.out.println(startsWithCorD.test(s3));
}
}true
true
false
Example 8:
package com.company;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
*
* Predicate with Stream filter
*
*/
public class PredicateExample8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee emp1 = new Employee(1,"John",34,2000);
Employee emp2 = new Employee(2,"Alex",22,5000);
Employee emp3 = new Employee(3,"Brian",23,5000);
Employee emp4 = new Employee(3,"Bob",23,7500);
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(emp1);
employeeList.add(emp2);
employeeList.add(emp3);
employeeList.add(emp4);
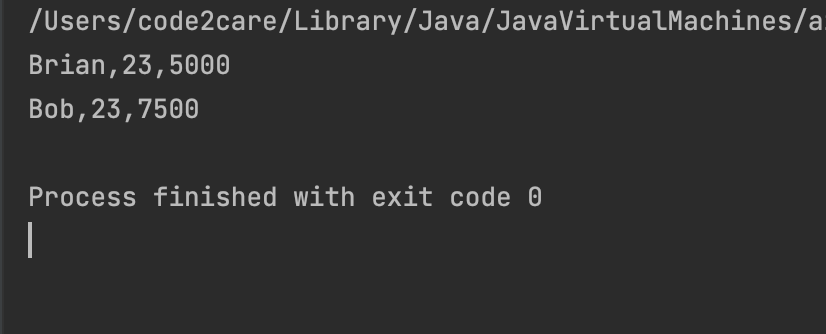
ArrayList<Employee> allEmpWithAgeGt22AndNameStartWithB = (ArrayList<Employee>) employeeList.stream().filter(emp -> emp.getEmpAge() > 22 && emp.getEmpName().startsWith("B")).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Employee emp: allEmpWithAgeGt22AndNameStartWithB) {
System.out.println(emp.getEmpName()+","+emp.getEmpAge()+","+emp.getEmpSalary());
}
}
static class Employee {
int empId;
String empName;
int empAge;
int empSalary;
public Employee(int empId, String empName, int empAge, int empSalary) {
this.empId = empId;
this.empName = empName;
this.empAge = empAge;
this.empSalary = empSalary;
}
public int getEmpId() {
return empId;
}
public void setEmpId(int empId) {
this.empId = empId;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
public int getEmpAge() {
return empAge;
}
public void setEmpAge(int empAge) {
this.empAge = empAge;
}
public int getEmpSalary() {
return empSalary;
}
public void setEmpSalary(int empSalary) {
this.empSalary = empSalary;
}
}
}
More Posts related to Java,
- Get the current timestamp in Java
- Java Stream with Multiple Filters Example
- Java SE JDBC with Prepared Statement Parameterized Select Example
- Fix: UnsupportedClassVersionError: Unsupported major.minor version 63.0
- [Fix] Java Exception with Lambda - Cannot invoke because object is null
- 7 deadly java.lang.OutOfMemoryError in Java Programming
- How to Calculate the SHA Hash Value of a File in Java
- Java JDBC Connection with Database using SSL (https) URL
- How to Add/Subtract Days to the Current Date in Java
- Create Nested Directories using Java Code
- Spring Boot: JDBCTemplate BatchUpdate Update Query Example
- What is CA FE BA BE 00 00 00 3D in Java Class Bytecode
- Save Java Object as JSON file using Jackson Library
- Adding Custom ASCII Text Banner in Spring Boot Application
- [Fix] Java: Type argument cannot be of primitive type generics
- List of New Features in Java 11 (JEPs)
- Java: How to Add two Maps with example
- Java JDBC Transition Management using PreparedStatement Examples
- Understanding and Handling NullPointerException in Java: Tips and Tricks for Effective Debugging
- Steps of working with Stored Procedures using JDBCTemplate Spring Boot
- Java 8 java.util.Function and BiFunction Examples
- The Motivation Behind Generics in Java Programming
- Get Current Local Date and Time using Java 8 DateTime API
- Java: Convert Char to ASCII
- Deep Dive: Why avoid java.util.Date and Calendar Classes
More Posts:
- How to fix Jenkins Plugin Stuck in Uninstallation pending Status - Linux
- Python: Merge DataFrames Pandas Outer Join Example - Python
- Cannot load PowerApps form in SharePoint Online due to repeated authentication - SharePoint
- Add scroll to div element in HTML Css - CSS
- Fix: Jupyter Notebook Black Web Page on Localhost - Python
- How to Change Bootstrap Carousel Slide Speed - Bootstrap
- How to create StackOverflow error in java - Java
- Efficient way to perform HTTP cURL GET/POST Requests with Payload - cURL