If you want to create a fine and write to it in a single command you can do it in various ways, one of the way is to use the echo command and use > redirect the text to a file, but doing so the file will be created and echoed text will be written to the file.
Example:
bash $ echo "This will be written to the file" > myFile.txt
bash $ cat myFile.txt
This will be written to the file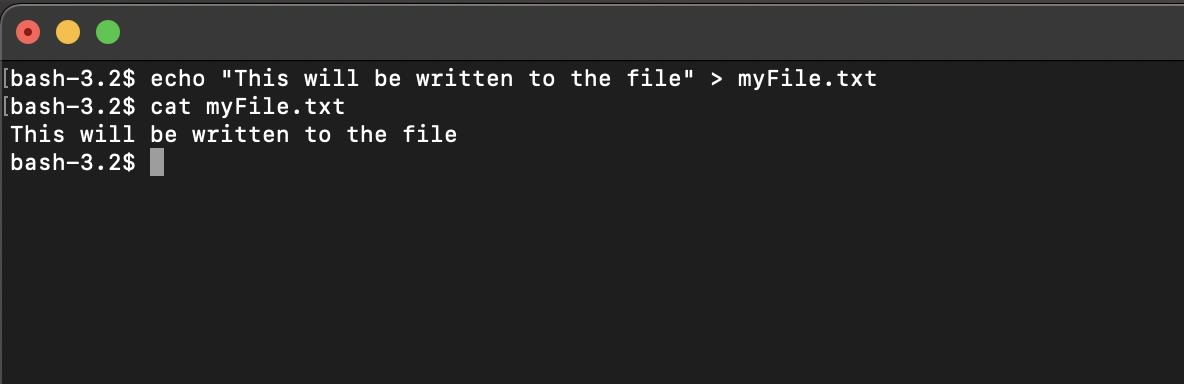
You can in this way also redirect the output of a command to a file.
Example:bash-3.2$ cd /
bash-3.2$ ls > /Users/code2care/Desktop/myFile.txt
bash-3.2$ cat /Users/code2care/Desktop/myFile.txt
Applications
Library
System
Users
Volumes
bin
cores
dev
etc
home
opt
private
sbin
tmp
usr
varComments:
- Thanks!
03 Jul 2022 17:07:05 GMT
- Further comments disabled!
More Posts related to Linux,
- Command to know the Available Memory on Linux System
- How to install curl on Alpine Linux
- How to backup a file in Linux/Unix
- Install Java Runtime Environment (Oracle or open JRE) on Ubuntu
- What is the Default Admin user and Password for Jenkins
- How to tar.gz a directory or folder Command
- Copy entire directory using Terminal Command [Linux, Mac, Bash]
- Fix: bash: ipconfig: command not found on Linux
- Command to check Last Login or Reboot History of Users and TTYs
- Linux: Create a New User and Password and Login Example
- ls command to list only directories
- bash: cls: command not found
- How to exit from nano command
- Installing and using unzip Command to unzip a zip file using Terminal
- What does apt-get update command does?
- ls command: sort files by name alphabetically A-Z or Z-A [Linux/Unix/macOS/Bash]
- How to remove or uninstall Java from Ubuntu using apt-get
- scp: ssh: connect to host xxxx port 22: Connection refused Error
- Sort ls command by last modified date and time
- Create Nested Directories using mkdir Command
- How to Exit a File in Terminal (Bash/Zsh)
- Command to know the installed Debian version?
- How to connect to SSH port other than default 22
- How to save a file in Nano Editor and Exit
- Install OpenSSL on Linux/Ubuntu
More Posts:
- How to remove or uninstall Java from Ubuntu using apt-get - Linux
- Word count in Notepad++ - NotepadPlusPlus
- Add Custom header and footer to Windows Notepad file - NotepadPlusPlus
- What is the Null Object Equivalent in Python? - Python
- Ping IP/Server Address using Python Example - Python
- How to know current Ubuntu Linux version via terminal command - Ubuntu
- Fix: TextEdit Open Html as Plain Text Code - MacOS
- How to update VIM version on a Mac - vi