In this tutorial, we will see how we can convert a Java byte array to String in three different ways,
Table of Content:Example 1: Using the String Object Constructor
//converting String to byte array
byte[] byteArray = "This is a byte array".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
//converting byte array to String
String str = new String(byteArray);
//converting String to byte array
byte[] byteArray = "This is a byte array".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
//converting byte array to String
String str = new String(byteArray);For the ease of a demo, we have converted a String to a byte array using the getBytes() method, we are constructing a new String by decoding the byte array,
Extract from String.java class, /**
* Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified array of bytes
* using the platform's default charset. The length of the new {@code
* String} is a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the
* Length of the byte array.
*
* The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid
* in the default charset is unspecified. The {@link
* java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control
* over the decoding process is required.
*
* @param bytes
* The bytes to be decoded into characters
*
* @since 1.1
*/
public String(byte[] bytes) {
this(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
}Example 2: Converting ASCII Byte Array to String
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class AsciiByteArrayToString {
public static void main(String... args) {
byte[] data = new byte[]{80,81,83,84,85,86};
System.out.println(new String(data,StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class AsciiByteArrayToString {
public static void main(String... args) {
byte[] data = new byte[]{80,81,83,84,85,86};
System.out.println(new String(data,StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}Output: PQSTUV
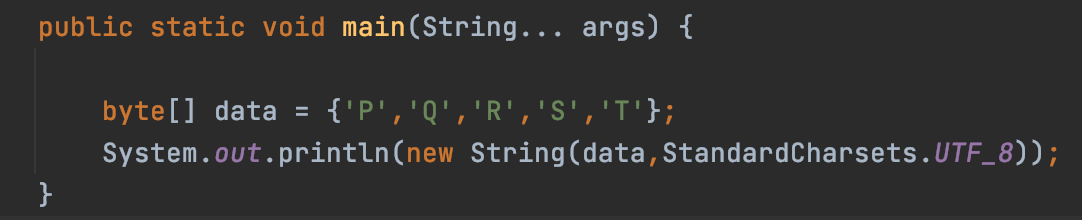
Example 3: Converting Char Byte Array to String
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class CharByteArrayToString {
public static void main(String... args) {
byte[] data = {'P','Q','R','S','T'};
System.out.println(new String(data,StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class CharByteArrayToString {
public static void main(String... args) {
byte[] data = {'P','Q','R','S','T'};
System.out.println(new String(data,StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}Output: PQSTUV
Facing issues? Have Questions? Post them here! I am happy to answer!
Author Info:
Rakesh (He/Him) has over 14+ years of experience in Web and Application development. He is the author of insightful How-To articles for Code2care.
Follow him on: X
You can also reach out to him via e-mail: rakesh@code2care.org