PHP tags : Tutorial
Usually PHP code is embedded into HTML code. To distinguish the start and end of PHP script we use the opening and
closing PHP tags.
<?php - is the opening PHP tag.
?> - is the closing PHP tag.
When a PHP file is parsed at the Server-end, the PHP Parser looks for the opening and the closing PHP tags.
Lets write a simple PHP file,
Every line that ends with a semi-colon is called as a Statement in PHP.
PHP echo statement is used to output Hello there! on the browser. When we run the above code we get the output as Hello there!.
If we save the above code as hello.php at the webserver, and request this file from a web browser, as this file has a .php extension it is first processed by the PHP Interpreter. The PHP Interpreter only executes the code between the opening and closing PHP tags, all code outside these tags is ignored. After interpreting the resulting code is delivered to the web browser as Pure Html code (i.e. there is no PHP code in the response).
We can have multiple PHP opening and closing tags in a file as shown in the below code snippet.
<?php - is the opening PHP tag.
?> - is the closing PHP tag.
When a PHP file is parsed at the Server-end, the PHP Parser looks for the opening and the closing PHP tags.
 |
The PHP parser only interprets the code between <?php ?> tags, rest of the code is ignored. <? ?> is also allowed (called as short tags) instead of <?php ?>, but it is not recommended. |
<html>
<head>
<body>
<h1>
<?php
echo "Hello there!";
?>
</h1>
</body>
</html>
The above code is a simplest PHP program. The php code is embedded between the H1 tag.Output
Hello there!
Every line that ends with a semi-colon is called as a Statement in PHP.
PHP echo statement is used to output Hello there! on the browser. When we run the above code we get the output as Hello there!.
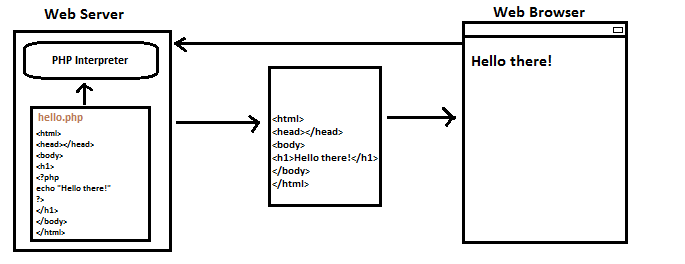 |
| The PHP file is interpreted at the Web Server by PHP interpreter before it is delivered to the Web Browser. |
If we save the above code as hello.php at the webserver, and request this file from a web browser, as this file has a .php extension it is first processed by the PHP Interpreter. The PHP Interpreter only executes the code between the opening and closing PHP tags, all code outside these tags is ignored. After interpreting the resulting code is delivered to the web browser as Pure Html code (i.e. there is no PHP code in the response).
We can have multiple PHP opening and closing tags in a file as shown in the below code snippet.
<?php echo "Hello there!"; ?> <?php echo "We can have multiple PHP tags in a file!"; ?>
Output
Hello there! We can have multiple PHP tags in a file!


