If you want to shutdown your Mac computer or Laptop (Macbook) using the Terminal command then you can make use of the shutdown or the halt command, note that this is special command and will require sudo rights in order to execute it.
Let's see few examples of this command,
Shutdown Mac using shutdown command
Let's read the manual first to understand this command and its syntax,
% man shutdown
NAME
shutdown -- close down the system at a given time
SYNOPSIS
shutdown [-] [-h [-u] | -r | -s | -k] [-o [-n]] time [warning-message ...]
DESCRIPTION
The shutdown utility provides an automated shutdown procedure for super-users to
nicely notify users when the system is shutting down, saving them from system administrators,
hackers, and gurus, who would otherwise not bother with such niceties,
The following options are available:
-h The system is halted at the specified time.
-k Kick everybody off. The -k option does not actually halt the system, but
leaves the system multi-user with logins disabled (for all but super-user).
-n If the -o is specified, prevent the file system cache from being flushed by passing
-n option to halt(8) or reboot(8). This option should probably not
be used.
-o If -h or -r is specified, shutdown will execute halt(8) or reboot(8) instead
of sending a signal to launchd(8).
-r The system is rebooted at the specified time.If you try the command without sudo you will get error: NOT super-user
% shutdown 5
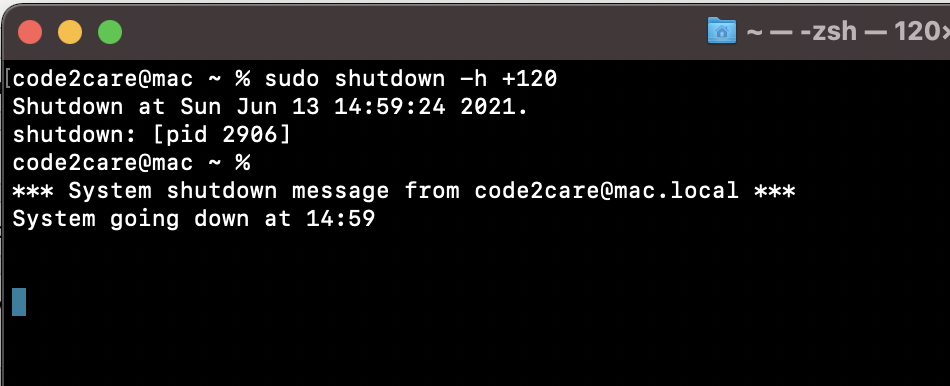
shutdown: NOT super-userLet's say you want to shutdown your Mac in the next 60 minutes (an hour) you can use the below command,
user@mac ~ % sudo shutdown -h 60
Password:
shutdown: bad time format
user@mac ~ % sudo shutdown -h +60
Shutdown at Sun Jun 13 13:48:36 2021.
shutdown: [pid 2875]
user@mac ~ %
*** System shutdown message from code2care@mac.local ***
System going down at 13:48 Note that if you do not provide the + sign for a time in minutes provided you will get an error saying bad time format. As you can see that a PID is provided to you as well as the exact time in HH:mm when the system will be shut down. If you wish to revoke this you can kill the process to avoid shutdown.
If you to instantly shutdown your Mac you can make use of the now option,
% sudo shutdown -h now
Shutdown Mac using halt or reboot command
Again, its also good to read the manual to better understand the command,
NAME
halt, reboot -- stopping and restarting the system
SYNOPSIS
halt [-lnqu]
reboot [-lnq]
DESCRIPTION
The halt and reboot utilities flush the file system cache to disk, send all running
processes a SIGTERM (and subsequently a SIGKILL) and, respectively, halt or restart
the system. The action is logged, including entering a shutdown record into the
wtmp(5) file.
When the system is halted with the halt command, the system is powered off.
The options are as follows:
-l The halt or reboot is not recorded in the system log. This option is
intended for applications such as shutdown(8), that call reboot or halt and
log this themselves.
-n The file system cache is not flushed. This option should probably not be
used.
-q The system is halted or restarted quickly and ungracefully, and only the
flushing of the file system cache is performed (if the -n option is not spec-
ified). This option should probably not be used.
-u The system is halted up until the point of removing system power, but waits
before removing power for 5 minutes so that an external UPS (uninterruptible
power supply) can forcibly remove power. This simulates a dirty shutdown to
permit a later automatic power on. OS X uses this mode automatically with
supported UPSs in emergency shutdowns.
Normally, the shutdown(8) utility is used when the system needs to be halted or
restarted, giving users advance warning of their impending doom and cleanly terminat-
ing specific programs.
% sudo halt
Have Questions? Post them here!
- How to show line numbers in Nano on Mac
- How to install Jupyter Notebook on macOS Sonoma
- How to Disable Remote Management using Mac Terminal
- Test internet speed using macOS Terminal command
- Docker Desktop needs privileged access macOS
- Google Search Hot Trends Screensaver for Mac OS X
- How to do calculations in Mac Terminal
- How to make TextEdit the default text Editor on Mac
- How to Show Full Website Address on Safari for Mac (Ventura/Sonoma)
- The Zsh Shell - Mac Tutorial
- Opening mac Terminal
- How to change the name of your Mac running on macOS Ventura 13
- How to find the Battery Cycle Count on macOS Ventura
- How to set an emoji as Zsh terminal prompt in macOS
- How to access Trash Folder using Mac Terminal Command
- macOS Ventura XCode Command Line Tools Installation
- Hide Bluetooth icon on Mac Menu Bar macOS Ventura 13
- How to run .sh file in Mac Terminal
- Terminal Command to get the list of available shells in macOS
- How to see Storage Information on macOS Ventura
- How to Go To /usr/local/bin on Mac Terminal?
- How to do screen recording on Mac
- How to Find File and Directory Size in Mac Terminal
- Open .bash_profile File in TextEdit using Terminal
- Remove Now Playing icon from macOS Big Sur Menu Bar
- Fix Generics: error unexpected type required: class found: type parameter - Java
- Fix: UnsupportedClassVersionError: Unsupported major.minor version 63.0 - Java
- How to add a Task List to Quick View Menu in SharePoint Online Site - SharePoint
- Install GitHub Command Line Tool on Mac - Git
- How to Write Code in Windows Notepad - Windows
- Working with Bluetooth on Mac Terminal using blueutil Commands - MacOS
- How to change Android EditText Cursor Color - Android
- Ubuntu: How to set Environment Variable - Ubuntu