Hello there! In this tutorial, we will cover step-by-step,
- Setting up Docker Desktop on Mac/Windows
- Downloading a Ubuntu Linux Image.
- Installing Git on Ununtu.
- Creating Dockerfile with Git pre-installed (recommended!)
- Creating a Local Git Repository.
- Committing code in Local Git Repository
- Creating a GitHub Account
- Generating GitHub Personal Access Token
- Push your local repo to GitHub
- Create Github repository
- Tutorial Summary!
- Downloading Docker Desktop
✏️ Note: If you already have Docker installed on your device, you can skip this step.
It is always better to work in a containerized environment when you are learning something as you do not want to mess around with your host operating system.
Docker is free for individual developers, students, and small businesses.
Steps to install Docker on Mac
There are multiple ways of installing Docker on a Mac, as a software developer, I would highly recommend making use of the HomeBrew package manager as this lets you install applications using the Terminal application.
Install Docker using HomeBrew Cask✏️ Note: If you do not have brew installed, you can follow the below link to get it installed first.
Installing Homebrew on MacWell, if you prefer to get Docker installed by downloading the setup file, follow the below steps,
- Go to docker.com
- Click on Download Docker Desktop
- The Docker.dmg will be downloaded
- Install it by following the instructions (this is for M1/M2 Mac, but if you have an Intel Chip Mac, the steps would be similar)
Steps to install Docker on Windows
- You must be on Windows 10 or 11 as a pre-requisite.
- Go to docker.com.
- Click on Download Docker Desktop (Windows)
- The Docker.dmg will be downloaded
- Double-Click on Docker Desktop Installer.exe and on the configuration page make sure to select WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V option.
You can also install the Docker Desktop using Powershell, from the folder where you have downloaded the setup run the below command,
Start-Process 'Docker Desktop Installer.exe' -Wait install
- Downloading a Ubuntu Linux Image
First, make sure Docker Desktop is running on your Mac/Windows system, on Terminal (if on macOS) or Command Prompt/PowerShell (on Windows), run the below command to download pull Ubuntu Linux image,
docker pull ubuntu:22.10 22.10: Pulling from library/ubuntu c2a61899dd54: Pull complete Digest: sha256:edc5125bd9443ab5d5c92096cf0e481f5e8cb12db9f5461ab1ab7a936c7f7d30 Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:22.10 docker.io/library/ubuntu:22.10 - Installing Git on Ubuntu
Now that we have Ubuntu Image downloaded, let's run the image,
docker run -i -t --name myUbuntuLinux ubuntu:22.10 root@72fa0cf98a34:/#Let us first update the package manager,
# apt-get updateNow its time to install the git package,
# apt-get install git .. .. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y .. Setting up git (1:2.37.2-1ubuntu1) ... .. doneYou can check if git is installed correctly by running the version command.
# git --version git version 2.37.2 - Installing Git on Ubuntu using Dockerfile (Recommended!)
Well, in step 3 we saw how to install Git after you run a Docker Ubuntu Container, in this step, we will create our own custom Docker image with Git preinstalled.
We are also going to have an external volume attached to it so that even when we relaunch our container the content of our git repository will persist
Dockerfile
FROM ubuntu:22.10 RUN mkdir /my-vol WORKDIR /my-vol RUN apt-get update RUN apt-get install git -y VOLUME /my-volCopy the above text in a file and save it with name dockerfile
Let us see each line of the dockerfile,
- FROM ubuntu:22.10: To create a new docker image from the Ubuntu image we downloaded.
- RUN mkdir /my-vol: To create a directory my-vol inside the docker container once it boots.
- WORKDIR /my-vol: When the container loads, we are moved to this directory and set it as the default working directory.
- RUN apt-get update: To update the package manager as we did earlier before installing Git.
- RUN apt-get install git -y: To install git, -y to automatic assume yes.
- VOLUME /my-vol: This is where we will mount our external volume (folder)
Let's build our custom image,
docker build -t 'my-ubuntu-git-img:1.0' .Now let's run our custom Docker image,
docker run -it -v /Users/c2c/myDir:/my-vol my-ubuntu-git-img:1.0Note: Replace /Users/c2c/myDir with the absolute path of a folder on your system (if on Windows eg. D:/folder1)
Again, we can check if Git is installed correctly by using the --version command,
root@713c170ae6ab:/my-vol# git --version git version 2.37.2 - Creating a Local Git Repository
We are all set to create our first Local Git Repository.
First let us create a directory called my-repo
# cd myrepoNow move inside the my-repo directory and run the git init command to initilize it as a git project,
# git init ... ... Initialized empty Git repository in /my-vol/my-repo/.git/ - Committing code in Local Git Repository
We are now good to do our first git commit,
# git commit --message "Initial Commit" [master (root-commit) b7d54e2] Initial Commit 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 index.htmlCongratulations! We are all set locally, now its time to move our code to GitHub.
- Creating a GitHub Account
Creating an account on GitHub is very simple and quick! Go to github.com and click on Sing-In, you will need to provide your email id and set a username.
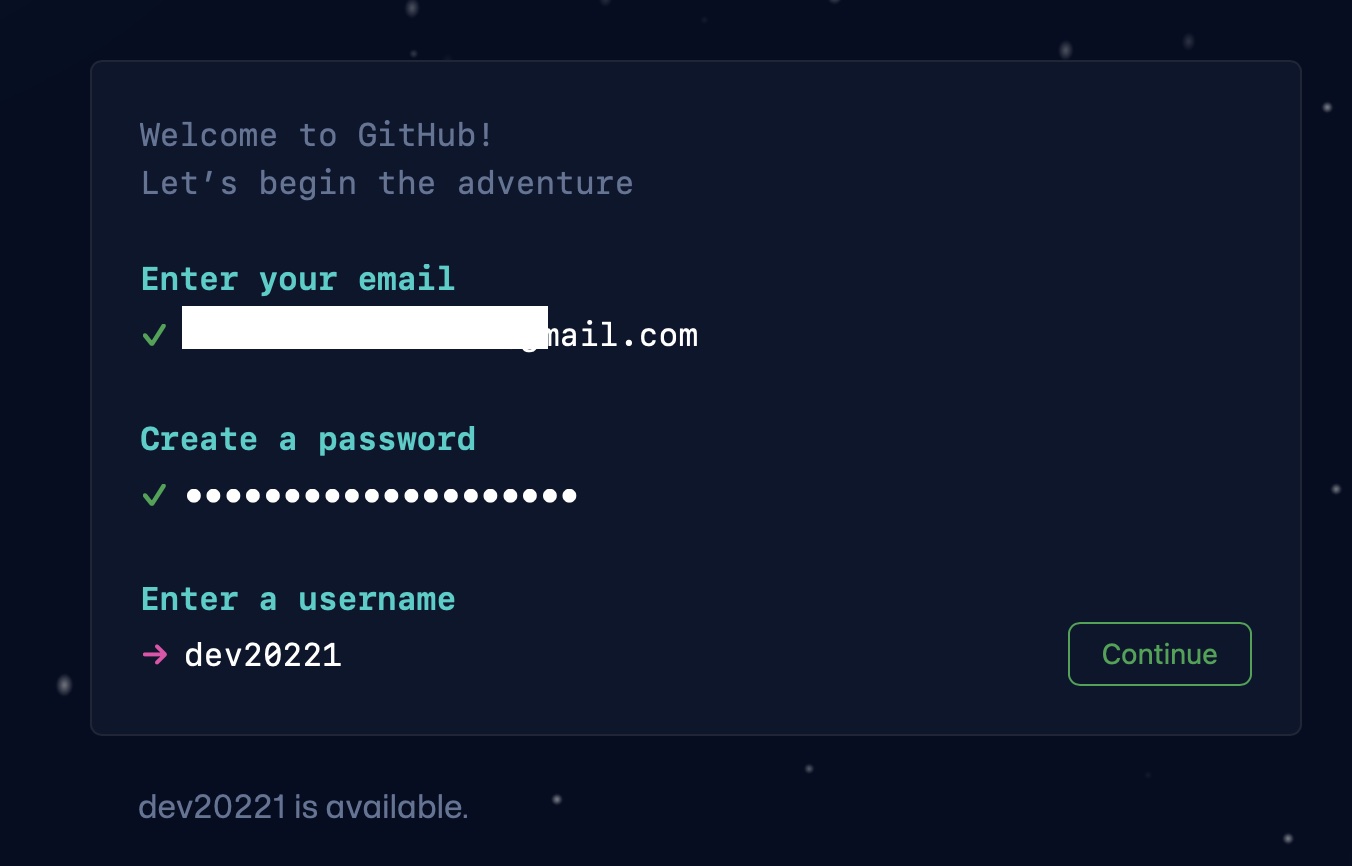
- Generating GitHub Personal Access Token
Before we can push our code up-stream to GitHub, we will need to generate a Personal Access Token,
Steps to create Personal Access Token
- Login to your GitHub account.
- Now Go to Profile -> Settings.
- Scroll down and select Developer Settings from the sidebar.
- Select Personal Access Tokens,
- Select on Generate Token (Classic)
- Add a note eg dev
- Scroll down and click on "Generate token"
- Copy the token and paste it into a text editor.
- Create Github repository
- Login to GitHub, go to https://github.com/new
- Add the repo name: my-repo (same as the one we just created locally)
- Select Public or Private (always private is an internal sensitive repo)
- Check "Add a README file",
- Click on Create Repo.
- Upload/Push Local Repo to GitHub
On the Ubuntu Linux Container, run the below git command after replacing,
access-token: the one we just created your-git-user: your GitHub username
Example:# git remote add origin https://access-token@github.com/your-github-user/my-repo.git# git remote add origin https://ghp_xxxxDgFlzSvzpC2xxxxx@github.com/code2care/my-repo.git - Tutorial Summary!
If you could follow all steps, well done! you have really achieved a lot, from creating a custom Docker image with Git pre-installed and then pushing your first git repo to GitHub!
Final Result: https://github.com/code2care/my-repo/tree/master
You can exit the docker container, by tying exit in the shell.
Let us create our first file as index.html and write the below text in it.
# echo "<h1>Hello World<h1>" > index.htmlBefore we move further we need to set the user and email for our git user,
# git config --global user.email "you@example.com"
# git config --global user.name "Your Name"Now let's add the file from the working directory to staging area,
# git add index.html